What is Impulse Control Disorder?
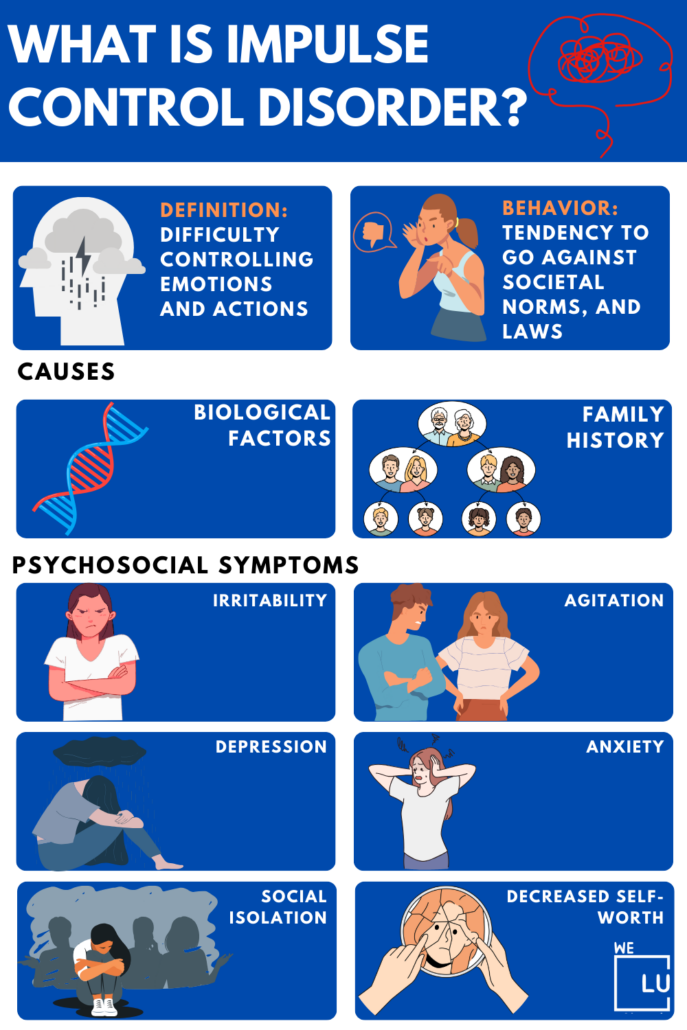
Impulse control disorder (ICD) is when someone has a hard time controlling their emotions and actions. People with impulse control problems often behave in ways that violate the rights of others and go against societal norms and laws.
It is challenging to identify impulse control disorders correctly. This can result in people needing more support. If we enhance our grasp of these disorders, we can bridge the gap in treatment and ensure individuals receive the care they need to manage symptoms. Treatment typically includes behavioral therapies, and medications might also be helpful.
What Causes Impulse Control Disorders?
As mental health experts haven’t pinpointed a precise cause for the development of impulse control disorders, there’s a shared understanding that these disorders arise from a combination of various factors. Here are examples of contributing factors:
- Biological Factors: Genetics and differences in brain structure and function can influence impulse control.
- Family History: If there’s a family history of impulse control disorders, there might be a genetic predisposition.
- Brain Chemistry: Imbalances in neurotransmitters, the brain’s chemical messengers, can contribute to impulsive behavior.
- Environmental Factors: Stressful life events, exposure to trauma, or a chaotic environment can increase the risk.
- Developmental Factors: Early childhood experiences and disruptions in normal development may contribute.
- Psychological Factors: Certain personality traits or mental health conditions can be linked to impulse control issues.
- Substance Abuse: Drug or alcohol abuse can impair judgment and contribute to impulsive actions.
What are Impulse Control Disorder Symptoms?
The symptoms of impulse-control disorder are influenced by age, environment, and gender. The following outlines a range of behavioral, physical, cognitive, and psychosocial symptoms that may suggest the presence of an impulse control disorder:
Psychosocial symptoms:
- Irritability.
- Agitation.
- Depression.
- Anxiety.
- Social isolation.
- Decreased self-worth.
- Periods of emotional detachment.
Physical symptoms:
- Injuries or scars from physical altercations.
- Burn marks in cases of fire-starting behaviors.
- Contracting sexually transmitted diseases due to risky sexual behaviors.
Behavioral symptoms:
- Compulsive lying.
- Aggressive or violent acts towards people, animals, objects, or property.
Cognitive symptoms:
- Obsessive thought patterns.
- Compulsive thought patterns.
- Difficulty controlling impulses.
- Impatience.

Skip To:
Learn More:
Effects of Impulsive Control Disorder
When symptoms of impulse control disorders are left untreated, they can lead to severe and enduring consequences, significantly impacting the person’s life. Potential effects include:
- Deterioration in academic performance.
- School suspension or expulsion.
- Challenges in forming and sustaining healthy interpersonal relationships.
- Engagement in self-harming behaviors.
- Legal involvement, potentially leading to incarceration.
- Continual decline in feelings of self-worth.
How are Impulse Control Disorders Diagnosed?
Diagnosing impulse control disorders typically involves a comprehensive assessment by mental health professionals. This process may include:
- Clinical Interviews: Detailed discussions with the individual, and often with family members or close associates, to gather information about behavior patterns and their impact.
- Diagnostic Criteria: Evaluation based on established criteria outlined in diagnostic manuals such as the DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition).
- Behavioral Observation: Monitoring and analyzing the individual’s behavior in various situations to identify impulsive patterns.
- Psychological Testing: Standardized tests to assess cognitive function, emotional well-being, and impulse control.
- Medical Examination: Ruling out any underlying medical conditions or substance-related factors that may contribute to impulsive behavior.
A thorough assessment helps create a comprehensive understanding of the individual’s symptoms, allowing for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning.
Get impulse control disorder counseling that works. Discover professional help from We Level Up Florida’s mental health therapists. Start getting support with a free call to our mental health hotline.
Get Help. Get Better. Get Your Life Back.
Searching for Accredited Dual Diagnosis Mental Health Centers Near You?
Even if therapy failed previously, or are in the middle of a difficult crisis, we stand ready to support you. Our trusted behavioral health specialists will not give up on you. When you feel ready or just want someone to speak to about counseling alternatives to change your life call us. Even if we cannot assist you, we will lead you to wherever you can get support. There is no obligation. Call our hotline today.
FREE 24/7 Dual Diagnosis Mental Health Services HotlineHow are Impulse Control Disorders Treated?
The treatment of impulse control disorders typically involves a combination of therapeutic approaches tailored to the individual’s specific needs. Standard treatment methods include:
- Behavioral Therapies: Targeted interventions to modify and manage impulsive behaviors, often employing techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT).
- Medications: In some cases, prescriptions may be prescribed to address underlying issues contributing to impulsivity, such as mood stabilizers or antidepressants.
- Support Groups: Participation in support groups or group therapy to share experiences and coping strategies with others facing similar challenges.
- Family Therapy: Involving family members in therapy to enhance understanding and support, as family dynamics can significantly impact impulse control issues.
- Skills Training: Teaching practical skills, such as stress management and problem-solving, to improve impulse control.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices to enhance self-awareness and emotional regulation, promoting better control over impulsive urges.
Treatment choice depends on the specific diagnosis, severity of symptoms, and individual circumstances. A multidisciplinary approach is often beneficial for comprehensive and effective management.
Impulse Control Disorder Therapies
Impulse Control Disorder Therapies
Several therapeutic approaches can be effective in managing impulse control disorders:
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors, helping individuals develop healthier coping mechanisms.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): Combines cognitive-behavioral techniques with mindfulness strategies, emphasizing acceptance and change to address impulsive behaviors.
- Behavioral Therapy: Targets specific behaviors, utilizing reinforcement and consequences to modify and replace impulsive actions with more adaptive alternatives.
- Psychodynamic Therapy: Explores unconscious patterns and unresolved conflicts contributing to impulsivity, aiming for insight and emotional regulation.
- Mindfulness-Based Interventions: Mindfulness meditation can improve self-awareness and impulse control.
- Group Therapy: Participating in group sessions with individuals facing similar challenges can provide support, encouragement, and shared coping strategies.
- Family Therapy: Involving family members helps address relational dynamics that may contribute to or exacerbate impulse control issues.
Therapeutic interventions are often tailored to the individual, considering the specific nature and severity of their impulse control disorder.
Impulse Control Disorder Medications
Impulse Control Disorder Medications
While therapy is a primary approach for managing impulse control disorders, certain medications may be prescribed to address underlying issues contributing to impulsive behavior. Common medications include:
- Mood Stabilizers: Such as lithium or anticonvulsant medications, which can help regulate mood and reduce impulsivity.
- Antidepressants: Especially selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or tricyclic antidepressants, which may be used if there’s a co-occurring mood disorder.
- Antipsychotics: In cases where impulsive behavior is associated with psychotic symptoms, antipsychotic medications may be considered.
- ADHD Medications: Stimulant medications like methylphenidate or amphetamines may be prescribed if there’s comorbid attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
A qualified healthcare professional must assess the individual’s situation and determine the most appropriate medication, if any. Prescription is often considered in conjunction with therapeutic interventions for comprehensive treatment.
Impulse Control Disorder Rehabilitation
Impulse Control Disorder Rehabilitation
Impulse control disorder rehabilitation is a comprehensive process aimed at helping individuals regain control over their impulsive behaviors. The program often involves a combination of therapeutic interventions, counseling, and skill-building exercises. Therapies are employed to address the underlying patterns of impulsive actions and replace them with healthier alternatives. These therapies often focus on enhancing self-awareness, identifying triggers, and developing coping strategies.
In addition to therapeutic interventions, impulse control disorder rehabilitation may incorporate medication management, especially when co-occurring conditions like mood disorders or ADHD are present. The rehabilitation process also emphasizes the importance of support networks involving family members and friends to provide encouragement, understanding, and assistance in implementing coping strategies in daily life.
We Level Up FL offers a comprehensive treatment approach to deal with impulse control disorder. Call our helpline for more information. Each call is free and confidential.
How to Deal With Impulse Control Disorder?
Managing impulse control disorders involves adopting practical strategies to enhance self-control. Here are some approaches:
- Mindfulness Techniques: Meditation and deep breathing can improve self-awareness and help individuals pause before acting impulsively.
- Cognitive Restructuring: Identify and challenge negative thought patterns contributing to impulsive behavior. Replace them with more rational and balanced thoughts.
- Developing Healthy Habits: Establishing routines and consistent patterns can promote stability and reduce the likelihood of impulsive actions.
- Stress Management: Learn effective stress-reduction techniques, such as exercise, yoga, or hobbies, to prevent stress from triggering impulsive behavior.
- Self-Monitoring: Keep a journal to track impulsive incidents, identifying patterns and triggers. This awareness can inform future preventive strategies.
- Social Support: Maintain connections with friends, family, or support groups. Having a support system can provide encouragement and understanding.
- Time-Outs: When feeling overwhelmed, take a break to calm down and reassess the situation before making impulsive decisions.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Develop effective problem-solving techniques to address challenges and frustrations without impulsive actions.
- Goal Setting: Establish realistic and achievable goals, breaking them down into smaller steps. This can provide a sense of accomplishment and reduce impulsive urges.
- Therapy: Engage in therapeutic interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), to learn specific coping skills and strategies for managing impulses.
It’s essential to work with mental health professionals to tailor strategies to individual needs and circumstances. Consistency and commitment to these strategies can significantly improve impulse control over time.
We Level Up FL Impulse Control Disorder Treatment Quick Tips
✅ Notice what situations or emotions lead to impulsive actions. Recognizing these triggers enables you to address them and find healthier coping methods.
✅ Build daily routines for stability, reducing the chance of spontaneous impulses. Having a predictable schedule is a vital tool for managing impulses.
✅ Talk to friends, family, or a mental health pro when you need understanding and help. A support system can guide and encourage you during impulsive moments.
Do you have questions about impulse control disorder or treatment in general? Call We Level Up FL helpline 24/7.

End the Emotional Pain. Get Your Life Back.
Feeling Depressed, Anxious or Struggling with Mental Health Illness? Get Safe Comfortable Mental Health Dual Diagnosis High-Quality Therapy From Counselors That Care. Begin Your Recovery Now.
Hotline (855) 940-6125




