Bipolar Disorder Therapies
Bipolar disorder, a complex and challenging mental health condition, affects millions worldwide. Characterized by extreme mood swings, from periods of intense mania to deep depressive episodes, it can significantly disrupt an individual’s life, relationships, and overall well-being. Fortunately, there is a ray of hope amidst this tumultuous storm – a variety of effective therapies tailored to address the unique needs of those with bipolar disorder.
In this article, we embark on a journey through the diverse landscape of bipolar disorder therapies. From traditional approaches to cutting-edge advancements, we aim to shed light on the range of treatment options available to patients, their families, and their support systems. Whether it’s providing stability during acute episodes, reducing the frequency of mood swings, or enhancing the overall quality of life, these therapies offer renewed optimism to those affected by this condition.
What is Bipolar Disorder?
Bipolar disorder, or manic-depressive illness, is a mental health condition characterized by extreme shifts in mood, energy levels, and behavior. Individuals with bipolar disorder experience episodes of mania, where they feel excessively high, energetic, and impulsive, and episodes of depression, characterized by overwhelming sadness, low energy, and a loss of interest in activities.
Bipolar disorder can significantly impact various aspects of a person’s life, including relationships, work or school performance, and overall quality of life. The frequency, duration, and intensity of mood episodes can vary from person to person, and the periods of stable mood between episodes are known as euthymia.
The exact causes of bipolar disorder are not fully understood, but research suggests a combination of genetic, biological, and environmental factors contribute to its development. Genetic factors play a significant role, as individuals with a family history of bipolar disorder are likelier to develop the condition.

Skip To:
Learn More:
- Is Bipolar a Personality Disorder? BPD vs. Bipolar
- 4 Common Bipolar Symptoms in Men, Signs, Tips, & Treatment
- Bipolar Disorder Medication, 8 Side Effects, and Effective Treatment
- Understanding How a Bipolar Person Thinks. What Does Bipolar Feel Like?
- What is Bipolar Psychosis? Symptoms, Cause, and Treatment.
- Guide to Bipolar Mixed Episode.
- Bipolar Disorder Therapies. Different Types of Effective Therapy for Bipolar Disorder
- Bipolar Symptoms In Women. Signs, Symptoms and Tips
- ADHD and Bipolar Disorder Guide.
- Is Bipolar a Disability? 5 Tips, Eligibility, and How to Claim.
Get Help. Get Better. Get Your Life Back.
Searching for Accredited Dual Diagnosis Mental Health Centers Near You?
Even if therapy failed previously, or are in the middle of a difficult crisis, we stand ready to support you. Our trusted behavioral health specialists will not give up on you. When you feel ready or just want someone to speak to about counseling alternatives to change your life call us. Even if we cannot assist you, we will lead you to wherever you can get support. There is no obligation. Call our hotline today.
FREE 24/7 Dual Diagnosis Mental Health Services HotlineWe Level Up Bipolar Disorder Mental Health Center Tip.
Bipolar disorder involves extreme mood swings, from highs (mania or hypomania) to lows (depression). It requires proper diagnosis and management. If you or someone you know experiences significant mood changes, seek professional help promptly. Treatment, including medication and therapy, can make a substantial difference. Ignoring symptoms or self-medicating can worsen the condition. Early intervention is key to a better quality of life.
Bipolar Disorder Facts Sheet
Bipolar Disorder:
- Mood Episodes: Characterized by distinct episodes of mania/hypomania and depression.
- Duration: Mood episodes can last for days, weeks, or months.
- Triggers: Episodes can occur without external triggers, and mood shifts are often unrelated to specific events.
- Self-Image: Individuals typically have a stable sense of self and identity.
- Impulsivity: Impulsive behaviors may occur during manic episodes.
- Treatment: Mood-stabilizing medications are often prescribed, along with psychotherapy.
Types of bipolar disorder:
There are several types of bipolar disorder, including:
- Bipolar I disorder: Characterized by manic episodes lasting at least seven days or severe manic symptoms requiring immediate hospitalization.
- Bipolar II disorder: Involves a pattern of depressive episodes and hypomanic episodes, but not full-blown mania.
- Cyclothymic disorder: Marked by numerous periods of hypomanic and depressive symptoms that last for at least two years (one year for children and adolescents).
Symptoms:
The symptoms of bipolar disorder vary depending on the mood episode:
- Manic episodes: Elevated mood, increased energy, racing thoughts, impulsivity, decreased need for sleep, excessive talking, grandiosity, and risky behavior.
- Hypomanic episodes: Similar to manic episodes but with less severity and a shorter duration.
- Depressive episodes: Persistent sadness, loss of interest or pleasure in activities, changes in appetite and sleep patterns, fatigue, feelings of guilt or worthlessness, difficulty concentrating, and thoughts of death or suicide.
Impact on daily life:
- Bipolar disorder can significantly impact various aspects of a person’s life, including relationships, work or school performance, and overall quality of life. However, with proper treatment and support, individuals with bipolar disorder can manage their symptoms effectively and lead fulfilling lives.
Bipolar Disorder Information (NIMH)
Bipolar Disorder Statistics
Understanding the role of genetics in bipolar disorder is crucial for gaining insights into the factors contributing to the condition’s development. Bipolar disorder is a complex mental health condition characterized by extreme mood swings between manic and depressive episodes. While the exact causes of bipolar disorder are still being explored, research has shown that genetic factors play a significant role.
In this article, we delve into the realm of bipolar disorder statistics, aiming to provide a comprehensive overview of its prevalence, demographic patterns, and the profound impact it has on individuals and society as a whole. By examining these statistics, we can gain valuable insights into the scale of the problem, identify potential risk factors, and highlight the importance of addressing bipolar disorder as a public health concern.
- Prevalence: According to the World Health Organization (WHO), bipolar disorder affects approximately 2.4% of the global population. It occurs equally among men and women and can develop at any age, although the typical age of onset is late adolescence to early adulthood.
- Lifetime Risk: The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) estimates that about 4.4% of adults in the United States will experience bipolar disorder at some point.
- Comorbidity: Bipolar disorder often co-occurs with other mental health conditions. Studies show that approximately 60-70% of individuals with bipolar disorder have at least one comorbid psychiatric disorder, such as anxiety disorders, substance use disorders, or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
2.4%
The global prevalence of bipolar disorder
Source: CDC
25 years
Bipolar disorder typically emerges in late adolescence or early adulthood
Source: NIMH
3:1
BPD is more commonly diagnosed in females
Source: NIH
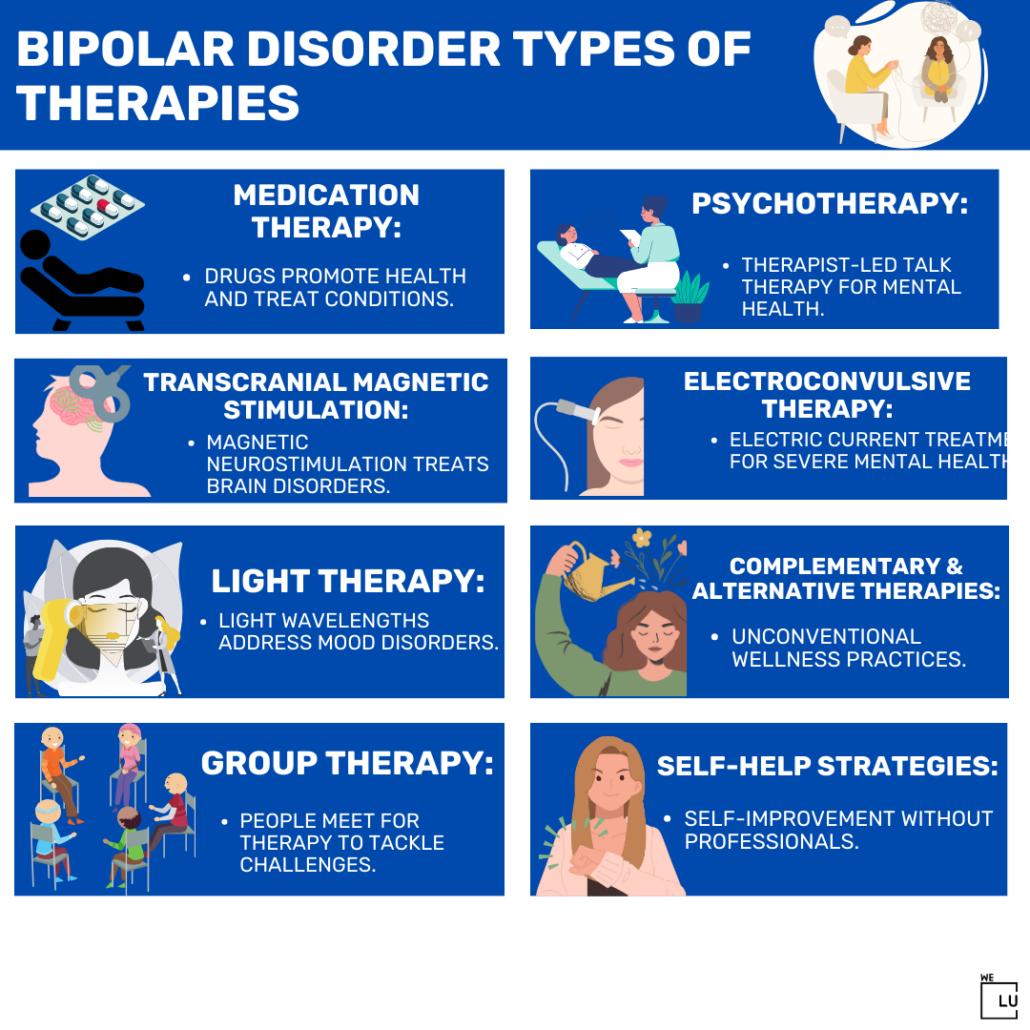
Bipolar Disorder Treatments
Bipolar disorder therapies encompass a wide range of treatment approaches to manage and stabilize the symptoms associated with bipolar disorder. These therapies can be classified into several categories.
It is crucial to remember that the effectiveness of each therapy varies from person to person, and treatment plans are often tailored to an individual’s specific needs and circumstances. Consulting with a mental health professional, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist, is essential to determine the most appropriate combination of therapies for managing bipolar disorder effectively.


End the Emotional Pain. Get Your Life Back.
Feeling Depressed, Anxious or Struggling with Mental Health Illness? Get Safe Comfortable Mental Health Dual Diagnosis High-Quality Therapy From Counselors That Care. Begin Your Recovery Now.
Hotline (855) 940-6125Types of Bipolar Disorder Therapy
- Medication Therapy: Medication is a fundamental component of bipolar disorder treatment. Mood stabilizers, such as lithium, valproate, and carbamazepine, are often prescribed to help control manic and depressive episodes. Antipsychotic medications may also be used to manage specific symptoms during acute phases.
- Psychotherapy (Talk Therapy):
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a widely used therapy that focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors contributing to mood swings. It helps individuals develop coping strategies and problem-solving skills.
- Family-focused therapy: This therapy involves family members in the treatment process and aims to improve communication, understanding, and support within the family unit.
- Interpersonal and Social Rhythm Therapy (IPSRT): IPSRT helps individuals stabilize daily routines and sleep patterns, as disruptions in these areas can trigger mood episodes.
- Psychoeducation: This type of therapy provides education about bipolar disorder, its symptoms, triggers, and treatment options to enhance understanding and self-management.
- Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT): ECT is a procedure where controlled electric currents are applied to the brain to induce a brief seizure. It is mainly used in severe cases of bipolar disorder when other treatments are ineffective.
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS): TMS is a non-invasive procedure that uses magnetic fields to stimulate specific brain areas. It is being investigated as a potential treatment for bipolar disorder, particularly for treatment-resistant patients.
- Light Therapy: Light therapy involves exposure to bright artificial light and is commonly used for managing seasonal affective disorder (SAD), a type of depression that occurs at specific times of the year. It may also benefit individuals with bipolar disorder, especially in managing depressive episodes.
- Complementary and Alternative Therapies: Some individuals may explore complementary approaches such as yoga, mindfulness meditation, acupuncture, or herbal supplements to complement traditional treatments. However, it is essential to consult healthcare professionals before incorporating these approaches into the treatment plan.
- Group Therapy: Group therapy involves individuals with bipolar disorder coming together in a supportive environment to share experiences and coping strategies and provide mutual support.
- Self-help Strategies: Individuals with bipolar disorder can learn and adopt various self-help techniques to manage their symptoms effectively. These may include stress reduction techniques, maintaining a mood diary, adhering to a regular sleep schedule, and avoiding substance abuse.
First-class Facilities & Amenities
World-class High-Quality Mental Health Services & Behavioral Health Substance Abuse Treatment
Rehab Centers TourRenowned Mental Health Centers. Serene Private Facilities. Inpatient Rehab Programs Vary.
Mental Health Helpline (855) 940-6125Proven recovery success experience, backed by a Team w/ History of:
15+
Years of Unified Experience
100s
5-Star Reviews Across Our Centers
10K
Recovery Successes
- Comprehensive Dual-Diagnosis Treatment
- Complimentary Family & Alumni Programs
- Coaching, Recovery & Development Events
- Comfortable Onsite Medical Detox Center
Risks of Therapy for Bipolar Disorder
While therapy for bipolar disorder can be highly beneficial, there are some potential risks and considerations that individuals should be aware of:

- Triggering Episodes: In some cases, therapy discussions, especially those involving emotional topics, may trigger mood episodes, such as manic or depressive states. It is crucial for both the individual and the therapist to closely monitor the emotional responses during therapy sessions to avoid exacerbating symptoms.
- Emotional Vulnerability: Therapy can bring up deep-seated emotions, which might be challenging for some individuals with bipolar disorder. This emotional vulnerability may lead to increased stress or even temporary worsening of symptoms before improvement occurs.
- Non-compliance: Some individuals may resist therapy or stop attending sessions, which can hinder progress and limit the effectiveness of the treatment.
- Misdiagnosis or Delayed Diagnosis: In some cases, bipolar disorder may be misdiagnosed or go undiagnosed for an extended period, leading to delays in appropriate treatment. A thorough and accurate assessment is essential for the right therapeutic approach.
- Therapist Inexperience: If a therapist is inexperienced or not well-versed in treating bipolar disorder, they may not provide the most effective interventions or support. Seeking therapy from a qualified mental health professional with experience in bipolar disorder is crucial.
- Interactions with Medication: Certain therapy techniques may interact with medication, potentially affecting their efficacy. The therapist must communicate and collaborate with the individual’s prescribing psychiatrist to ensure a cohesive treatment plan.
- Dependency on Therapy: While therapy is valuable, individuals may become overly dependent on it for managing their symptoms, neglecting other essential aspects of their treatment plan, such as medication adherence.
- Financial Burden: The cost of therapy can be a concern for some individuals, especially if they do not have adequate insurance coverage. This financial burden may limit their access to regular and consistent therapy sessions.
Bipolar Disorder Supportive Therapy
Bipolar disorder supportive therapy, also known as supportive psychotherapy, is a type of talk therapy that focuses on providing emotional support, encouragement, and understanding to individuals with bipolar disorder. Unlike specific therapeutic approaches that target specific symptoms or behaviors, supportive therapy aims to foster a supportive and empathetic therapeutic relationship to help individuals cope with the challenges of bipolar disorder.
The main objectives of bipolar disorder supportive therapy include:
- Emotional Support: The therapist provides a safe and non-judgmental space for individuals to express their feelings, emotions, and concerns about their bipolar disorder. The therapist helps individuals feel heard and validated by offering empathy and understanding.
- Validation and Normalization: The therapist acknowledges the struggles and difficulties of bipolar disorder, helping individuals feel less isolated and normalizing their experiences. This can reduce feelings of shame or self-blame.
- Coping Strategies: While not as structured as specific therapeutic modalities, supportive therapy may still provide general coping strategies to help individuals manage their symptoms and navigate challenging situations.
- Stress Reduction: Supportive therapy can assist individuals in developing stress-reduction techniques and lifestyle adjustments to minimize potential triggers for mood episodes.
- Medication Adherence: The therapist can discuss the importance of medication adherence and help individuals understand the role of medication in managing bipolar disorder symptoms.
- Enhancing Self-Esteem: Through positive reinforcement and encouragement, supportive therapy can help individuals build self-esteem and self-confidence, even when facing bipolar disorder’s challenges.
- Improving Communication: Supportive therapy may address communication difficulties in personal relationships, helping individuals develop healthier ways of expressing their needs and emotions.
It is essential to note that bipolar disorder supportive therapy is not a substitute for evidence-based treatments like medication and other structured forms of psychotherapy, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) or Interpersonal and Social Rhythm Therapy (IPSRT). Instead, it complements these treatments by providing emotional support and encouragement, enhancing an individual’s overall well-being and adherence to their treatment plan.
The therapeutic relationship is a vital aspect of supportive therapy, and the trust and rapport built between the therapist and the individual can significantly contribute to its effectiveness. By fostering a supportive and compassionate environment, individuals with bipolar disorder can feel empowered and better equipped to manage their condition and lead fulfilling lives.
World-class, Accredited, 5-Star Reviewed, Effective Mental Health Dual Diagnosis Programs. Complete Integrated Inpatient Rehab with Free Post Discharge Therapy Planning.
CALL (855) 940-6125End the Emotional Pain Rollercoaster. Gain Stability & Happiness Through Recovery Treatment. Start Mental Health Counseling Today. Get Free No-obligation Guidance by Behaviroal Health Specialists Who Understand Mental Health Recovery.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Bipolar Disorder
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for bipolar disorder is a structured and evidence-based psychotherapy that focuses on identifying and modifying negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with the condition. It is often used as an adjunctive treatment alongside medication to help individuals manage their symptoms, reduce the risk of relapse, and improve overall quality of life.
The fundamental principles and components of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for bipolar disorder include:
- Thought Monitoring: In CBT, individuals learn to identify and track their thoughts, particularly those related to mood changes, triggers, and stressors. By becoming aware of negative thought patterns and distortions, they can work towards challenging and reframing these thoughts in a more balanced and realistic way.
- Behavioral Activation: CBT aims to increase engagement in positive and fulfilling activities, even during depressive episodes. By encouraging individuals to participate in enjoyable and meaningful activities, CBT helps counteract the tendency to withdraw and isolate during depressive phases.
- Identifying Triggers and Warning Signs: Individuals learn to recognize specific triggers and early warning signs of mood episodes, be it manic, hypomanic, or depressive. By identifying these cues, they can take preventive actions and implement coping strategies to manage their symptoms effectively.

Ketamine Therapy for Bipolar Disorder Therapies
Ketamine therapy is an experimental treatment being studied for bipolar disorder and involves the administration of ketamine, a dissociative anesthetic, to alleviate symptoms during depressive episodes. Ketamine therapy is an emerging and experimental treatment being investigated for its potential benefits in managing bipolar disorder, particularly during depressive episodes. Ketamine, a dissociative anesthetic, is administered intravenously in controlled and supervised settings.
The therapy’s mechanism of action differs from traditional antidepressant medications, as ketamine targets the brain’s glutamate system, potentially leading to rapid and transient improvement in depressive symptoms. While research on ketamine therapy for bipolar disorder is ongoing, early studies have shown promising results in relieving individuals who have not responded well to conventional treatments. However, the long-term efficacy and safety of ketamine therapy for bipolar disorder require further investigation, and its use remains restricted to specialized clinical settings under the supervision of trained medical professionals.
Bipolar Androgen Therapy
Bipolar Androgen Therapy refers to a medical approach that involves the administration of androgens, which are male sex hormones such as testosterone, to individuals with bipolar disorder. The rationale behind this therapy is based on the observation that androgens may have mood-stabilizing effects in some individuals. However, it’s essential to note that bipolar androgen therapy is still a subject of ongoing research and is not considered a standard or established treatment for bipolar disorder.
This therapy’s potential risks and benefits need further investigation before it can be widely recommended or incorporated into standard treatment protocols for bipolar disorder. As with any experimental treatment, it should only be considered under the guidance and supervision of qualified medical professionals in a clinical research setting.
Experience Transformative Recovery at the We Level Up Treatment Center.
See our authentic success stories. Get inspired. Get the help you deserve.



Start a New Life
Begin with a free call to a behavioral health treatment advisor. Learn more about our dual-diagnosis programs. The We Level Up treatment center network delivers recovery programs that vary by each treatment facility. Call to learn more.
- Personalized Care
- Caring Accountable Staff
- World-class Amenities
- Licensed & Accredited
- Renowned w/ 5-Star Reviews
We’ll Call You
Popular Bipolar Disorder Therapies FAQs
-
What are some popular bipolar disorder therapies?
Some popular therapies used to treat bipolar disorder include Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Interpersonal and Social Rhythm Therapy (IPSRT), Family-focused therapy, and Medication Therapy (using mood stabilizers and antipsychotics).
Related Question: Best Therapy for Bipolar Disorder -
How effective is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for bipolar disorder?
CBT has shown effectiveness in helping individuals with bipolar disorder manage their symptoms, improve coping skills, and reduce the risk of relapse. It focuses on identifying and modifying negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with the condition.
8 Steps & Tips for Maintaining Your Mental Wellbeing Informative Video
Video Script
We at We Level Up FL are dedicated to personalized mental health services tailored to each person’s unique needs. Our experienced team collaborates closely with clients to create therapy programs that address their challenges and align with their goals. With empathy and support, we empower individuals to take an active role in their mental health journey by providing tools and strategies. We encourage exploration, self-discovery, and growth in a safe and nurturing environment. We understand that everyone is different, so we listen attentively and develop customized therapy plans based on individual concerns, strengths, and aspirations.
Search Drug & Alcohol Rehab / Detox & Mental Health Bipolar Disorder Therapies. Treatments for Bipolar Disorder Topics & Resources
Sources
- National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) – Bipolar Disorder: https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/bipolar-disorder/ Learn More: Bipolar Disorder Therapies
- NIMH – Borderline Personality Disorder: https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/borderline-personality-disorder/ Learn More: Therapies for Bipolar Disorder
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) – Bipolar Disorder: https://www.samhsa.gov/find-help/disorders/bipolar-disorder Learn More: Bipolar Therapy
- SAMHSA – Borderline Personality Disorder: https://www.samhsa.gov/find-help/disorders/borderline-personality-disorder Learn More: Bipolar Disorder Therapies
- National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) – Bipolar Disorder: https://www.nami.org/About-Mental-Illness/Mental-Health-Conditions/Bipolar-Disorder Learn More: Bipolar Disorder Therapies.
- NAMI – Borderline Personality Disorder: https://www.nami.org/About-Mental-Illness/Mental-Health-Conditions/Borderline-Personality-Disorder Learn More: Bipolar Disorder Therapies
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – Mental Health – Bipolar Disorder: https://www.cdc.gov/mentalhealth/basics/bipolar.html Learn More: Bipolar Disorder Therapies.
- CDC – Mental Health – Borderline Personality Disorder: https://www.cdc.gov/mentalhealth/basics/borderline.html Learn More: Bipolar II Disorder Therapies, Bipolar Disorder Family Therapy
- Office on Women’s Health (OWH) – Bipolar Disorder: https://www.womenshealth.gov/mental-health/mental-health-conditions/bipolar-disorder Learn More: Bipolar Disorder Therapies