Is Bipolar a Disability?
Living with bipolar disorder can present unique challenges that may impact various aspects of an individual’s life. It raises important questions about whether bipolar disorder qualifies as a disability and the options available to those seeking support.
Knowing your rights is vital if bipolar disorder makes it hard to hold your employment. Although having bipolar disorder can qualify you for disability or SSI, it is not an automatic process. Find out if you qualify and how to make the most of the aid offered to you.
Bipolar Disorder Disability Acts
No specific law or act is called the “Bipolar Disability Act.” However, various laws and acts protect the rights of individuals with disabilities, including those with bipolar disorder. These laws aim to ensure equal opportunities, accessibility, and protection against discrimination. Here are some fundamental rules and acts that are relevant in the context of bipolar disorder and disability:
- Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA): The Americans with Disabilities Act is a comprehensive law in the United States that prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities in various areas of public life. It ensures equal access to employment, public accommodations, transportation, government services, and telecommunications. The ADA protects individuals with bipolar disorder from discrimination and requires reasonable accommodations in the workplace and other settings.
- Rehabilitation Act of 1973: The Rehabilitation Act prohibits discrimination based on disability in programs and activities receiving federal financial assistance. Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act protects individuals with disabilities, including bipolar disorder, from discrimination in educational institutions, federal agencies, and federally funded programs.
- Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI): SSDI is a federal program in the United States that provides disability benefits to individuals who have paid into the Social Security system and cannot work due to a qualifying disability, including bipolar disorder.
- Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act (MHPAEA): The MHPAEA requires health insurance plans to provide equal coverage for mental and substance use disorder services as they do for physical health services. This act aims to prevent discrimination in insurance coverage and ensure that individuals with bipolar disorder access necessary mental health treatments and services.
What is Disability?
When a person’s physical, mental, sensory, or cognitive abilities are severely diminished, we say they have a disability. It’s a problem that makes it hard to go about daily living, whether moving about, talking to other people, learning new things, feeling emotionally stable, or anything else. There is a vast spectrum of disabilities, from readily apparent, such as mobility issues or blindness, to those that are not, such as chronic pain, mental health issues, or developmental disabilities.
In the context of disability for bipolar disorder, it is crucial to recognize that bipolar disorder can be viewed as a disabling condition that may affect an individual’s capacity to perform in various settings. Manic and depressive episodes are hallmarks of bipolar disorder, a mental health illness characterized by dramatic shifts in mood. Mood swings can profoundly affect a person’s thinking, feeling, and doing.
Society can take steps toward developing inclusive environments that provide required accommodations and support networks for people with bipolar illness if it acknowledges the condition as potentially detrimental. Implementing laws and procedures that provide equal opportunities and access to services for people with bipolar disorder and other impairments is a crucial step in this direction.
Can You Get Disability for Bipolar?
Having bipolar disorder may make you eligible for disability payments. The severity of your symptoms and how they impact your capacity to work are usually the determining factors in your eligibility. You must provide medical evidence, including mental health doctors’ documents, to apply for disability compensation. The Social Security Administration (SSA) will determine if you are disabled based on their criteria. To complete the application process, it is recommended that you seek the advice of a legal or medical advisor.
5 Tips on Claiming Disability for Bipolar Disorder
- Gather Comprehensive Medical Documentation: When making a disability claim for bipolar disorder, it’s essential to gather comprehensive medical documentation that supports your case. This includes psychiatric evaluations, treatment records, medication history, therapy notes, and other relevant medical reports. These documents provide evidence of your diagnosis, treatment history, and the impact bipolar disorder has on your daily functioning.
- Maintain Consistent Treatment: Consistent treatment is crucial when claiming disability for bipolar disorder. It demonstrates your commitment to managing your condition and highlights the ongoing need for medical intervention. Follow your treatment plan, attend regular appointments with mental health professionals, and comply with prescribed medications. Adhering to treatment can strengthen your case and show that you seek to improve your condition.
- Keep a Symptom Journal: Keeping a symptom journal can be highly beneficial when claiming disability for bipolar disorder. Documenting your symptoms, including mood fluctuations, episodes of mania or depression, and the impact these symptoms have on your daily life provides tangible evidence of how bipolar disorder affects your functioning. Include details such as duration, frequency, and any functional impairments you experience.
- Consult with a Disability Attorney or Advocate: Seeking guidance from a disability attorney or advocate can significantly increase your chances of a successful disability claim. They are experienced in navigating the complex process, understanding the legal requirements, and presenting your case effectively. A professional can assist you in gathering the necessary documentation, filling out forms correctly, and representing your interests throughout the application and appeals process.
- Be Prepared for Appeals and Reviews: Disability claims for bipolar disorder may be initially denied or require periodic reviews to determine ongoing eligibility. It’s essential to be prepared for these possibilities. Understand the appeals process and the steps involved in challenging a denial decision. Keep your medical records current, attend evaluations or hearings when required, and promptly respond to requests for additional information. If necessary, a proactive approach and seeking legal advice can help you navigate these challenges effectively.

Skip To:
Learn More:
- Is Bipolar a Personality Disorder? BPD vs. Bipolar
- 4 Common Bipolar Symptoms in Men, Signs, Tips, & Treatment
- Bipolar Disorder Medication, 8 Side Effects, and Effective Treatment
- Bipolar Disorder Therapies. Different Types of Effective Therapy for Bipolar Disorder
- Understanding How a Bipolar Person Thinks. What Does Bipolar Feel Like? Signs and Symptoms of Bipolar Disorder
- ADHD and Bipolar Disorder Guide. ADHD Vs Bipolar. Bipolar and ADHD Symptoms. Bipolar Vs ADHD Diagnosis. ADHD Bipolar Treatments.
- Understanding Rapid Cycling Bipolar Disorder. Symptoms, and Effective Treatments.
- Lithium for Bipolar Disorder, Understanding Side Effects and Potential Risks
- Is Bipolar Disorder Genetic? Understanding the Risks of your Family History
Are you Bipolar?
If you suspect you have bipolar disorder or want to understand your mental health better, taking this self-assessment can be a valuable first step.
At We Level Up Mental Health Center, you’ll find a supportive environment where you can work on managing impulsive behaviors, improving emotional regulation, and developing healthier coping mechanisms for bipolar disability.
Get Help. Get Better. Get Your Life Back.
Searching for Accredited Dual Diagnosis Mental Health Centers Near You?
Even if therapy failed previously, or are in the middle of a difficult crisis, we stand ready to support you. Our trusted behavioral health specialists will not give up on you. When you feel ready or just want someone to speak to about counseling alternatives to change your life call us. Even if we cannot assist you, we will lead you to wherever you can get support. There is no obligation. Call our hotline today.
FREE 24/7 Dual Diagnosis Mental Health Services HotlineTips and Strategies on Managing your Bipolar Disorder
✅ Medication Consistency: Stick to your prescribed medications and routines. They play a vital role in mood stability.
✅ Routine & Sleep: Maintain a regular daily schedule, including quality sleep. It’s a powerful mood stabilizer.
✅ Identify Triggers: Recognize your mood triggers, like stress or lack of sleep, and develop strategies to cope effectively.
✅ Support Network: Build a strong support network. Friends, family, and mental health professionals can be your allies on this journey.
Remember, small steps can lead to significant progress. Stay committed, and take each day as it comes. You’ve got this!
Bipolar Disorder Fact Sheet
Bipolar Disorder
- Mood Episodes: Characterized by distinct episodes of mania/hypomania and depression.
- Duration: Mood episodes can last for days, weeks, or months.
- Triggers: Episodes can occur without external stimuli, and mood shifts are often unrelated to specific events.
- Self-Image: Individuals typically have a stable sense of self and identity.
- Impulsivity: Impulsive behaviors may occur during manic episodes.
- Treatment: Mood-stabilizing medications are often prescribed, along with psychotherapy.
Types of Bipolar Disorder
There are several types of bipolar disorder, including:
- Bipolar I disorder: Characterized by manic episodes lasting at least seven days or severe manic symptoms requiring immediate hospitalization.
- Bipolar II disorder: Involves a pattern of depressive episodes and hypomanic episodes, but not full-blown mania.
- Cyclothymic disorder: This is marked by numerous periods of hypomanic and depressive symptoms that last for at least two years (one year for children and adolescents).
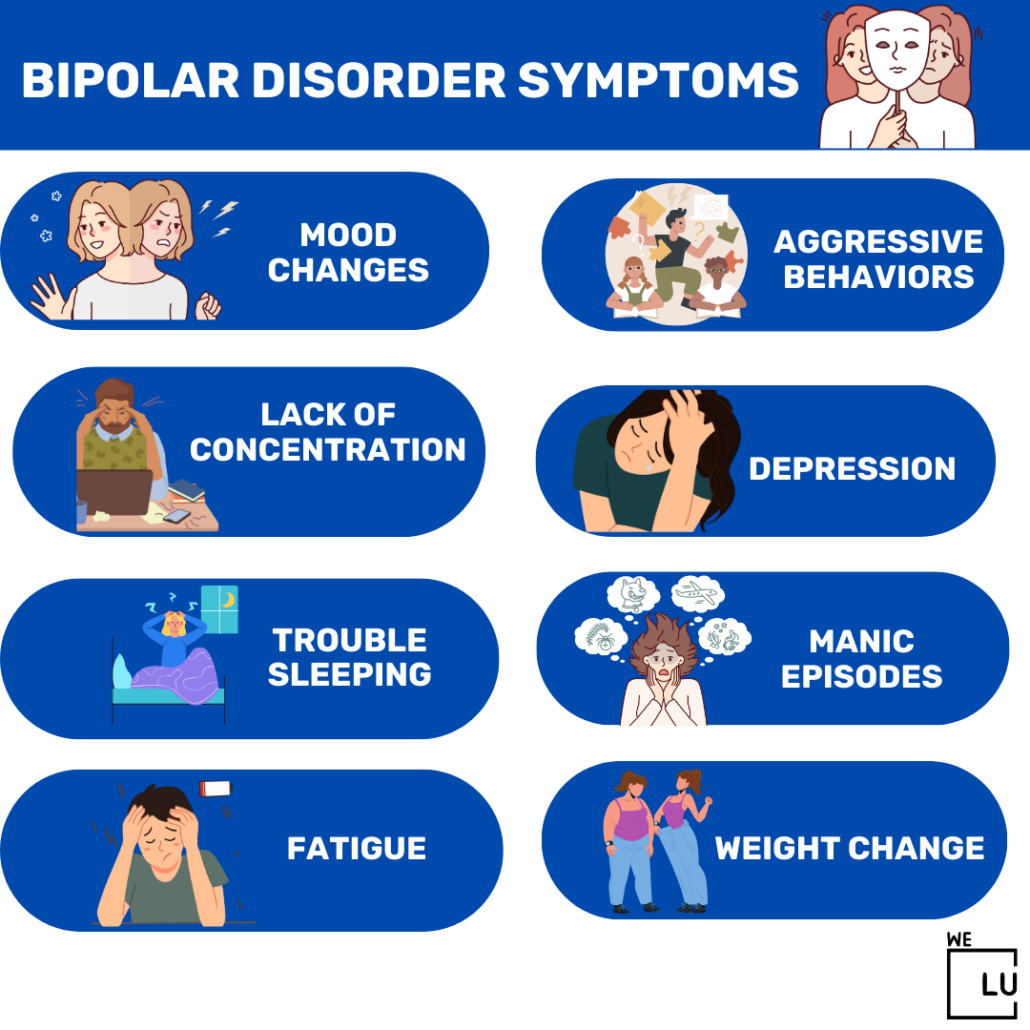
Symptoms
The symptoms of bipolar disorder vary depending on the mood episode:
- Manic episodes: Elevated mood, increased energy, racing thoughts, impulsivity, decreased need for sleep, excessive talking, grandiosity, and risky behavior.
- Hypomanic episodes: Similar to manic episodes but with less severity and a shorter duration.
- Depressive episodes: Persistent sadness, loss of interest or pleasure in activities, changes in appetite and sleep patterns, fatigue, feelings of guilt or worthlessness, difficulty concentrating, and thoughts of death or suicide.
Impact on daily life
- Bipolar disorder can significantly impact various aspects of a person’s life, including relationships, work or school performance, and overall quality of life. However, with proper treatment and support, individuals with bipolar disorder can manage their symptoms effectively and lead fulfilling lives.
Understanding Bipolar Disorder PDF Download
Bipolar Disorder Statistics
Bipolar disorder is a complex mental health condition affecting millions worldwide. Characterized by alternating periods of intense mood swings, ranging from elevated states of mania to episodes of profound depression, bipolar disorder can significantly impact a person’s daily functioning, relationships, and overall quality of life.
- Prevalence: According to the World Health Organization (WHO), bipolar disorder affects approximately 2.4% of the global population. It occurs equally among men and women and can develop at any age, although the typical age of onset is late adolescence to early adulthood.
- Lifetime Risk: The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) estimates that about 4.4% of adults in the United States will experience bipolar disorder at some point.
- Comorbidity: Bipolar disorder often co-occurs with other mental health conditions. Studies show that approximately 60-70% of individuals with bipolar disorder have at least one comorbid psychiatric disorder, such as anxiety disorders, substance use disorders, or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
2.4%
The global prevalence of bipolar disorder.
Source: CDC
25 years
Bipolar disorder typically emerges in late adolescence or early adulthood.
Source: NIMH
3:1
BPD is more commonly diagnosed in females.
Source: NIH
Social Security for Bipolar Disorder Disability
Bipolar disorder can significantly hinder an individual’s ability to secure or maintain employment. As of December 2017, 34.6% of disability recipients qualified based on mental health conditions. The Social Security Administration maintains a comprehensive list of impairments determining an individual’s eligibility for disability benefits. Within this listing, Section 12 is dedicated to mental disorders, and specifically, Section 12.04 pertains to mood disorders, including bipolar disorder.
Section 12.04 of the Social Security Administration describes mood disorders as conditions characterized by mood disturbances accompanied by complete or partial manic or depressive syndromes. In this context, mood signifies an enduring emotional state that influences one’s overall mental life, typically involving prolonged depression or elevated mood.
To be eligible for benefits, individuals with a mental disorder must meet the requirements outlined in sections A and B or fulfill all the criteria in section C.

End the Emotional Pain. Get Your Life Back.
Feeling Depressed, Anxious or Struggling with Mental Health Illness? Get Safe Comfortable Mental Health Dual Diagnosis High-Quality Therapy From Counselors That Care. Begin Your Recovery Now.
Hotline (855) 940-6125Standard Exceptions of Bipolar and Disability
An employer may refuse to provide accommodations for one of two reasons:
- Suppose the employer can demonstrate that granting an accommodation would result in undue hardship for the company. This could include accommodations that are excessively costly, extensive, substantial, or disruptive or that would fundamentally alter the nature or operation of the business. Factors such as the company’s size, financial resources, and other relevant considerations are considered.
- If the employee is considered a direct threat to their safety or the safety of others in the workplace.
Suppose you face a situation where accommodation is denied. In that case, your employment is terminated for one of these reasons, or if you believe you’ve experienced discrimination due to your condition, you can file a claim with the EEOC within 180 days of the denial or violation. You can do this online or by requesting an application from your nearest EEOC office. The employer must respond to the claim and provide reasons for not making the accommodation or considering the employee a workplace safety risk.
For individuals struggling with bipolar psychosis, We Level Up Mental Health Center offers specialized and compassionate bipolar disorder treatment.
First-class Facilities & Amenities
World-class High-Quality Mental Health Services & Behavioral Health Substance Abuse Treatment
Rehab Centers TourRenowned Mental Health Centers. Serene Private Facilities. Inpatient Rehab Programs Vary.
Mental Health Helpline (855) 940-6125Proven recovery success experience, backed by a Team w/ History of:
15+
Years of Unified Experience
100s
5-Star Reviews Across Our Centers
10K
Recovery Successes
- Comprehensive Dual-Diagnosis Treatment
- Complimentary Family & Alumni Programs
- Coaching, Recovery & Development Events
- Comfortable Onsite Medical Detox Center
Bipolar Disability Benefits

The process of obtaining bipolar disability benefits can be complex and time-consuming. Many applications are initially denied, and appeals may be necessary. It’s advisable to consult with professionals, understand the specific requirements of the disability programs, and consider seeking legal advice to navigate the process successfully. Bipolar disorder can be a disabling condition that significantly affects a person’s ability to work and function in various areas of life. As a result, individuals with bipolar disorder may be eligible for disability benefits to provide financial assistance and support. Here are some key points to consider regarding bipolar disability benefits:
- Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI): In the United States, individuals with bipolar disorder may qualify for Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) benefits. SSDI provides financial support to individuals who have paid into the Social Security system through their work history. To be eligible, you must meet specific criteria, including severe impairment that prevents you from performing substantial gainful activity and meeting the duration requirements.
- Supplemental Security Income (SSI): Another disability benefit program in the United States is Supplemental Security Income (SSI). SSI provides financial assistance to individuals with limited income and resources, including those with disabilities. Eligibility for SSI is based on financial need and meeting the medical criteria for a disabling condition such as bipolar disorder.
- Application Process: Applying for bipolar disability benefits typically involves applying to the Social Security Administration (SSA). The application requires detailed information about your medical condition, treatment history, work history, and functional limitations. It’s crucial to provide thorough and accurate documentation, including medical records and supporting statements from healthcare professionals.
- Medical Evidence: Medical evidence is crucial in approving disability benefits for bipolar disorder. It’s essential to have comprehensive documentation of your diagnosis, treatment history, and the functional limitations caused by the condition. This includes psychiatric evaluations, therapy records, hospitalizations, medication records, and other relevant medical reports.
- Consultation with Professionals: Seeking assistance from professionals experienced in disability claims, such as disability attorneys or advocates, can greatly enhance your chances of a successful application. They can guide you through the process, help gather necessary evidence, and ensure your case is presented effectively.
World-class, Accredited, 5-Star Reviewed, Effective Mental Health Dual Diagnosis Programs. Complete Integrated Inpatient Rehab with Free Post Discharge Therapy Planning.
CALL (855) 940-6125End the Emotional Pain Rollercoaster. Gain Stability & Happiness Through Recovery Treatment. Start Mental Health Counseling Today. Get Free No-obligation Guidance by Behaviroal Health Specialists Who Understand Mental Health Recovery.
Eligibility Guidelines on Bipolar Disability
An individual with a mental disorder becomes eligible for benefits by meeting the criteria outlined in sections A and B or fulfilling all the requirements in section C (see below).
A. This entails the medically documented persistence of one of the following:
- A depressive syndrome is characterized by at least four of the following:
- Anhedonia or pervasive loss of interest in almost all activities.
- Appetite disturbance resulting in a weight change.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Psychomotor agitation or retardation.
- Decreased energy.
- Feelings of guilt or worthlessness.
- Difficulty concentrating or thinking.
- Thoughts of suicide.
- Hallucinations, delusions, or paranoid thinking.
- A manic syndrome is characterized by at least three of the following:
- Hyperactivity.
- Pressure of speech.
- Flight of ideas.
- Inflated self-esteem.
- Decreased need for sleep.
- Easy distractibility.
- Involvement in activities has a high probability of painful consequences that are not recognized.
- Hallucinations, delusions, or paranoid thinking.
- Bipolar disorder with a history of episodic periods that manifest a complete symptomatic picture of both manic and depressive syndromes (and currently characterized by either or both syndromes).
B. The condition should result in at least two of the following:
- Marked restriction of activities of daily living.
- Significant difficulties in maintaining social functioning.
- Considerable difficulties in maintaining concentration, persistence, or pace.
- Repeated episodes of decompensation, each of extended duration.
C. A medically documented history of a chronic affective disorder lasting for at least two years has caused more than minimal limitations in the ability to perform basic work activities, with symptoms or signs currently alleviated by medication or psychosocial support. In this case, one of the following should apply:
- Repeated episodes of decompensation, each of extended duration.
- A residual disease process that has resulted in such marginal adjustment that even a minimal increase in mental demands or environmental changes is predicted to lead to decompensation.
- A history of one or more years of inability to function outside a highly supportive living arrangement indicates the continued need for such an environment.
Social Security encompasses specific rules tailored to mental health issues. If you enlist an attorney’s services, ensure they are well-versed in these regulations.
Social Security may not always approve disability benefits for individuals with severe mental health conditions. In numerous instances, initial applications are denied. Consequently, individuals with mental health conditions and their advocates (knowledgeable psychiatrists, therapists, and attorneys) must meticulously prepare and document their cases and exhibit persistence. If necessary, seek assistance in filing—your doctor or support groups may recommend valuable resources.
Experience Transformative Recovery at the We Level Up Treatment Center.
See our authentic success stories. Get inspired. Get the help you deserve.



Start a New Life
Begin with a free call to a behavioral health treatment advisor. Learn more about our dual-diagnosis programs. The We Level Up treatment center network delivers recovery programs that vary by each treatment facility. Call to learn more.
- Personalized Care
- Caring Accountable Staff
- World-class Amenities
- Licensed & Accredited
- Renowned w/ 5-Star Reviews
We’ll Call You
Popular Is Bipolar a Disability FAQs
-
Can you get a disability for bipolar disorder?
Bipolar disability benefits are attainable. Meeting particular requirements and showing that your bipolar illness seriously hinders your capacity to work and function in everyday life is required to qualify for disability payments like SSDI or SSI. Medical documents and country-specific disability program standards are needed to apply. Disability claim experts can assist through the procedure.
-
Is being bipolar a disability?
Yes, having bipolar disorder might be regarded as a kind of disability.
-
does bipolar qualify for disability?
Bipolar disorder can qualify for disability if it meets specific criteria outlined by Social Security.
-
is bipolar 2 a disability?
Bipolar 2, like bipolar 1, can qualify as a disability if it fulfills the necessary conditions.
-
is bipolar 1 a disability?
Bipolar 1 is considered a disability if it meets the requirements for disability benefits.
-
is bipolar depression a disability?
Bipolar depression may be considered a disability when it significantly impairs an individual’s ability to work and daily functioning.
-
how do get disability for bipolar?
To get a disability for bipolar disorder, you must meet the criteria specified by the Social Security Administration and provide thorough documentation.
-
does bipolar count as a disability?
Bipolar disorder counts as a disability if it meets the criteria set by Social Security.
-
Is bipolar 1 disability?
Bipolar 1 can be considered a disability if it meets the requirements for disability benefits.
8 Steps & Tips for Maintaining Your Mental Wellbeing Informative Video
Video Script
We at We Level Up FL are dedicated to personalized mental health services tailored to each person’s unique needs. Our experienced team collaborates closely with clients to create therapy programs that address their challenges and align with their goals. With empathy and support, we empower individuals to take an active role in their mental health journey by providing tools and strategies. We encourage exploration, self-discovery, and growth in a safe and nurturing environment. We understand that everyone is different, so we listen attentively and develop customized therapy plans based on individual concerns, strengths, and aspirations.
Search We Level Up FL Is Bipolar a Disability? 5 Tips, Eligibility, & How to Claim Resources
Sources:
- Fairclough S, Robinson RK, Nichols DL, Cousley S. In sickness and in health: Implications for employers when bipolar disorders are protected disabilities. Employee Responsibilities and Rights Journal. 2013;25(4):277-292. doi:10.1007/s10672-013-9221-2 Can I get a disability for bipolar? Is bipolar considered a disability? related articles
- U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission. The ADA: Your Responsibilities as an Employer. Is bipolar disorder considered a disability? Does bipolar disorder qualify for disability
- Americans with Disabilities National Network. Southwest Ada Center. The ADA National Network Disability Law Handbook. Is being bipolar considered a disability? Is bipolar disorder a disability?
- U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission. Enforcement Guidance on the ADA and Psychiatric Disabilities. Can you get on disability for bipolar? Can you get disability for bipolar depression-related articles
- Social Security Administration. Annual Statistical Report on the Social Security Disability Insurance Program, 2017. is bipolar a mental disability? related articles