Non-Stimulant ADHD Medication
In ADHD treatment, stimulant medications have long taken center stage, relieving individuals grappling with attention deficits and hyperactivity. However, the landscape of ADHD management is far from monolithic. For adults seeking alternatives or experiencing challenges with stimulant-based approaches, non-stimulant ADHD medications present a valuable avenue worth exploring.
This article delves into non-stimulant ADHD medication explicitly tailored for adults. With a focus on addressing the unique needs, concerns, and considerations of the adult population, we embark on a journey to understand the effectiveness, mechanisms, benefits, and potential drawbacks of this alternative approach. Whether you’re an adult diagnosed with ADHD or a healthcare professional seeking comprehensive insights, this guide sheds light on the intricacies of non-stimulant medications as a viable option for managing ADHD symptoms effectively.
ADHD Medication Side Effects
Stimulant Medications:
- Decreased appetite and weight loss: Stimulant medications can suppress appetite, leading to weight loss. Ensuring a balanced diet and regular monitoring of weight is crucial.
- Sleep disturbances: Stimulants may disrupt sleep patterns, causing difficulty falling or staying asleep. Taking medications earlier in the day or adjusting the dosage can help manage this issue.
- Increased heart rate and blood pressure: Some individuals may experience an elevation in heart rate and blood pressure. Regular monitoring and consultation with a healthcare professional are essential, particularly for those with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions.
- Mood changes: Stimulant medications can occasionally induce mood swings, irritability, or anxiety. Open communication with the prescribing doctor can help determine the best action.
- Tics: In rare cases, stimulant use may exacerbate existing tics or trigger new ones. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help evaluate the risks and benefits.
Non-Stimulant Medications:
- Gastrointestinal issues: Non-stimulant medications may cause stomachaches, nausea, or constipation. Staying hydrated, consuming fiber-rich foods, and discussing these symptoms with a doctor can aid in managing gastrointestinal discomfort.
- Drowsiness and fatigue: Some individuals may experience drowsiness or fatigue as a side effect. Adjusting the dosage or timing of medication intake in consultation with a healthcare professional can help mitigate these effects.
- Mood changes: Non-stimulant medications are sometimes associated with mood or emotional regulation changes. Open communication with the prescribing doctor is crucial to address any concerns.

Skip To:
Learn More:
- How to Find ADHD Doctors Near Me? Effective ADHD Therapy Options.
- ADHD Medication, Side Effects, Mechanism, and Effectiveness
- Executive Dysfunction ADHD. What It Is, Symptoms & Treatment.
- ADHD and Bipolar Symptoms and Signs. Differences Between ADHD vs Bipolar in Adults vs Children, Diagnosis & Treatment.
- Is ADHD Genetic? What You Need to Know
ADHD Medication for Adults
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental condition that transcends age, affecting children and adults. While it’s often associated with childhood, a significant portion of those diagnosed with ADHD continues to experience its challenges well into adulthood. The demands of daily life, work responsibilities, and personal relationships can compound the impact of ADHD symptoms in adults.
Thankfully, medical science has evolved to provide a range of treatments tailored to the unique needs of adults with ADHD. Medication, in particular, has emerged as a cornerstone of managing ADHD symptoms effectively. From enhancing focus and concentration to mitigating impulsivity and hyperactivity, ADHD medication for adults promises to unlock newfound control and empowerment.
Get Help. Get Better. Get Your Life Back.
Searching for Accredited Dual Diagnosis Mental Health Centers Near You?
Even if therapy failed previously, or are in the middle of a difficult crisis, we stand ready to support you. Our trusted behavioral health specialists will not give up on you. When you feel ready or just want someone to speak to about counseling alternatives to change your life call us. Even if we cannot assist you, we will lead you to wherever you can get support. There is no obligation. Call our hotline today.
FREE 24/7 Dual Diagnosis Mental Health Services HotlineADHD Fact Sheet
Prevalence: ADHD is one of the most common neurodevelopmental disorders, affecting approximately 5-10% of children and 2-5% of adults worldwide. It is more commonly diagnosed in males than females.
Core Symptoms: The core symptoms of ADHD include inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Individuals with ADHD may have difficulty sustaining attention, organizing tasks, following instructions, sitting still, and controlling impulses.
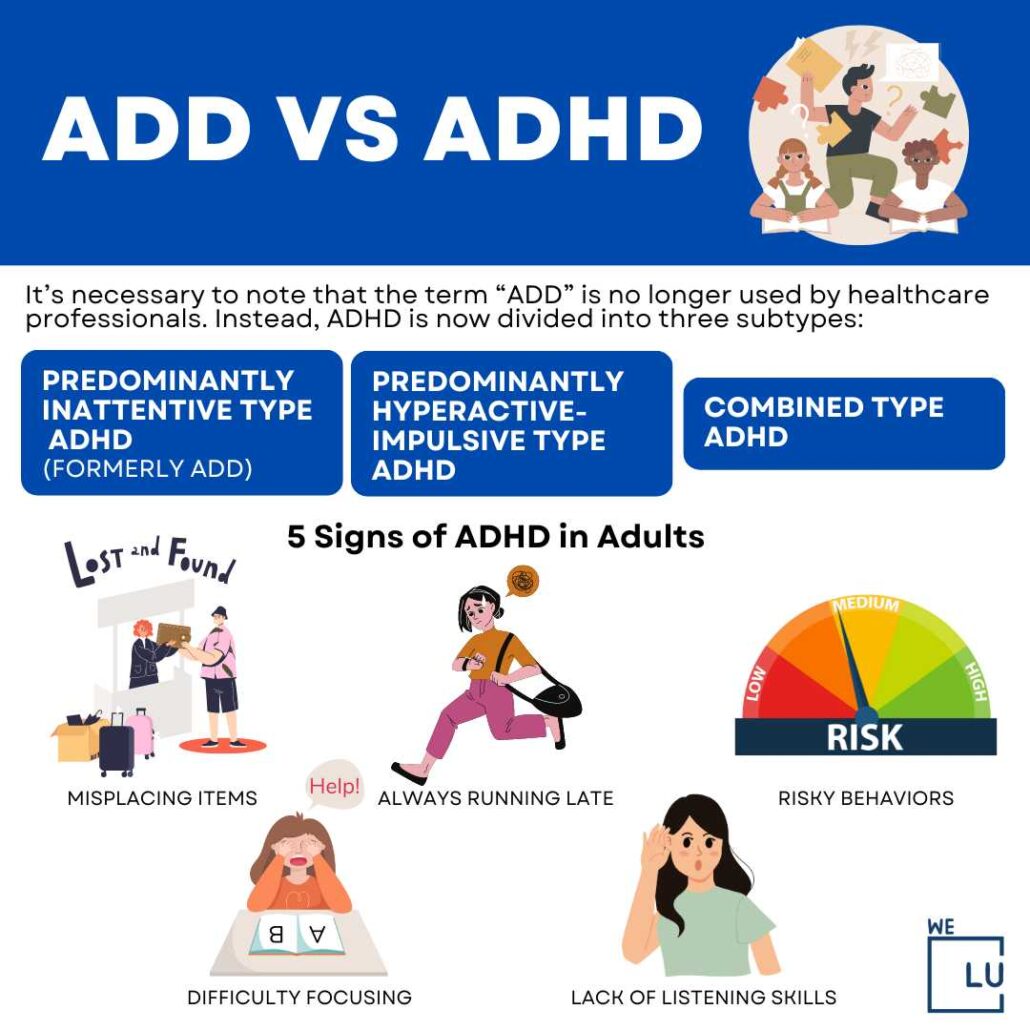
ADHD is categorized into three subtypes:
a. Predominantly Inattentive Presentation: Primarily characterized by difficulties with attention and organization.
b. Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive Presentation: Primarily characterized by hyperactivity and impulsivity.
c. Combined Presentation: Displays symptoms of both inattention and hyperactivity-impulsivity.
Diagnosis of ADHD: This involves a comprehensive evaluation, including interviews with the individual, parents (for children), and teachers or other relevant observers. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) criteria are commonly used for diagnosis.
Long-Term Outlook: With appropriate diagnosis, treatment, and support, individuals with ADHD can lead fulfilling lives. Early intervention and ongoing management can significantly reduce the impact of symptoms and improve overall functioning.
Co-occurring Conditions: ADHD often coexists with other conditions such as learning disabilities, anxiety disorders, depression, oppositional defiant disorder (ODD), and conduct disorder (CD). These comorbidities can further complicate diagnosis and treatment.
Non-Stimulant ADHD Medication Statistics
Understanding ADHD treatment involves delving into the diverse array of medications available and the prevalence and usage patterns associated with these treatments. While stimulant medications often dominate discussions on ADHD management, non-stimulant options are crucial for individuals who may not respond well to stimulants or have specific medical considerations.
This section explores non-stimulant ADHD medication statistics, shedding light on the utilization, trends, and broader context surrounding these alternative treatment approaches. By delving into the statistical insights related to non-stimulant medications, we understand their role within the larger ADHD treatment spectrum. From usage percentages to specific medication preferences, this exploration aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of non-stimulant medications’ impact on addressing the challenges of ADHD.
- Non-Stimulant Medication Usage: Non-stimulant medications are often considered when stimulant medications are ineffective or unsuitable due to individual health conditions. As of my last update, non-stimulant medications were estimated to be prescribed for around 20-25% of individuals with ADHD.
- Efficacy and Tolerability: Non-stimulant medications are considered adequate for some individuals who don’t respond well to stimulants or have contraindications to their use. Their effectiveness and tolerability vary widely from person to person, making it essential to find the proper medication through trial and consultation with a healthcare professional.
- Combined Therapy: In some cases, non-stimulant medications are used with stimulant medications or behavioral therapies to address specific symptoms or challenges.
8.7 Million
In 2019, the number of visits to physician offices with attention deficit disorder as the primary diagnosis was 8.7 million.
Source: NIMH
9.5%
Approximately 9.5% of American adults, ages 18 and over, will suffer from a depressive illness (major depression, bipolar disorder, or dysthymia) each year.
Source: NIMH
70-80%
The heritability of ADHD, estimated to be around 70-80%, further supports the notion that genetic factors play a substantial role in its development.
Source: NIMH
Best ADHD Medication for Adults
Determining the “best” ADHD medication for adults can be complex and highly individualized, as different medications can affect different people differently. The choice of medication depends on factors such as the individual’s specific ADHD symptoms, medical history, potential side effects, and response to different medications. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional, preferably a psychiatrist or a medical doctor with expertise in ADHD, to determine the most appropriate medication for a particular adult.
That being said, there are two main categories of ADHD medications presented in a table commonly prescribed for adults: stimulant medications and non-stimulant medications.

| Medication Type | Examples | How They Work |
|---|---|---|
| Stimulant Medications | Methylphenidate-based (e.g., Ritalin, Concerta) | Increase neurotransmitter levels for improved focus and impulse control |
| Amphetamine-based (e.g., Adderall, Vyvanse) | Enhance attention and cognitive function | |
| Non-Stimulant Medications | Atomoxetine (Strattera) | Selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor |
| Guanfacine (Intuniv) | Alpha-2 adrenergic agonist for reduced impulsivity | |
| Clonidine (Kapvay) | Affects certain brain receptors for symptom control |
Remember that medication is often just one part of a comprehensive ADHD management plan, which might also include therapy, lifestyle adjustments, and other supportive strategies.

End the Emotional Pain. Get Your Life Back.
Feeling Depressed, Anxious or Struggling with Mental Health Illness? Get Safe Comfortable Mental Health Dual Diagnosis High-Quality Therapy From Counselors That Care. Begin Your Recovery Now.
Hotline (855) 940-6125Non-Stimulant ADHD Medication Names
These non-stimulant medications work differently from stimulants and aim to address the symptoms of ADHD, such as impulsivity, inattention, and hyperactivity, by targeting various neurotransmitter systems in the brain. They are typically considered when stimulant medications are ineffective or unsuitable for an individual’s medical history or preferences.
Some common non-stimulant ADHD medication names include:
- Atomoxetine (Strattera): Atomoxetine is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. It helps increase the availability of norepinephrine in the brain, improving attention, focus, and impulse control.
- Guanfacine (Intuniv): Guanfacine is an alpha-2 adrenergic agonist that affects certain receptors in the brain. It can help reduce hyperactivity, impulsivity, and distractibility.
- Clonidine (Kapvay): Clonidine, also an alpha-2 adrenergic agonist, has been found to have benefits in managing ADHD symptoms, particularly hyperactivity and impulsivity.
- Bupropion (Wellbutrin): While primarily used as an antidepressant, bupropion is sometimes prescribed off-label for ADHD. It affects dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the brain, potentially improving attention and mood.
- Tricyclic Antidepressants: Medications like imipramine and desipramine are tricyclic antidepressants that can be used to manage ADHD symptoms. They impact neurotransmitter activity and can help address inattention and impulsivity.
Non-stimulant ADHD medications often have a slower onset of action than stimulants and might require several weeks to achieve full effects. They also come with their own set of potential side effects and considerations. Choosing the appropriate medication involves careful consideration of an individual’s medical history, symptom profile, and potential benefits and risks associated with each option.
It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional before starting any ADHD medication regimen, as they can provide personalized guidance based on an individual’s specific needs and circumstances.
First-class Facilities & Amenities
World-class High-Quality Mental Health Services & Behavioral Health Substance Abuse Treatment
Rehab Centers TourRenowned Mental Health Centers. Serene Private Facilities. Inpatient Rehab Programs Vary.
Mental Health Helpline (855) 940-6125Proven recovery success experience, backed by a Team w/ History of:
15+
Years of Unified Experience
100s
5-Star Reviews Across Our Centers
10K
Recovery Successes
- Comprehensive Dual-Diagnosis Treatment
- Complimentary Family & Alumni Programs
- Coaching, Recovery & Development Events
- Comfortable Onsite Medical Detox Center
Over the Counter ADHD Medications for Adults

No over-the-counter (OTC) medications are specifically approved for treating ADHD in adults. Unlike certain conditions where OTC options exist, such as pain relief or allergy medications, the management of ADHD typically requires prescription medications.
Effective treatment for ADHD usually involves stimulant or non-stimulant medications, available only by prescription. Stimulant medications, such as methylphenidate (Ritalin) or amphetamine-based drugs (Adderall), are the most commonly prescribed medications for ADHD. Non-stimulant medications, such as atomoxetine (Strattera) or guanfacine (Intuniv), are alternatives that may be used in specific cases.
Remember that self-medication or reliance on over-the-counter medications without professional guidance may not be an effective treatment for ADHD and may carry risks. To ensure the healthiest and m
Best ADHD Medication for Adults with Anxiety and Depression
Finding the most suitable ADHD medication for adults struggling with anxiety and depression can be complex. This combination of conditions requires carefully addressing ADHD symptoms while not exacerbating anxiety and depression. Working closely with a knowledgeable healthcare professional, ideally a psychiatrist, who can evaluate the individual’s needs and tailor the treatment plan accordingly is essential.
Here are some considerations and potential options for adults with ADHD, anxiety, and depression:
1. Selective Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs):
SNRIs like venlafaxine and duloxetine are commonly prescribed for individuals with ADHD and comorbid anxiety and depression. They can address ADHD symptoms while also providing some relief for anxiety and depression. However, it’s essential to monitor for potential side effects and interactions.
2. Bupropion (Wellbutrin):
Bupropion is an atypical antidepressant that affects both dopamine and norepinephrine. It’s sometimes prescribed off-label for ADHD and can particularly benefit individuals with depression. However, its effect on anxiety varies from person to person.
3. Atomoxetine (Strattera):
Atomoxetine is a non-stimulant medication approved for ADHD in adults. It can address ADHD symptoms and might be suitable for individuals with anxiety and depression due to its norepinephrine-based mechanism. However, discussing its use with a healthcare professional is essential, as it can also affect mood.
4. Combination Therapy:
In some cases, a combination of medications might be considered. For instance, an antidepressant targeting anxiety and depression could be paired with a carefully chosen ADHD medication. This approach requires close monitoring to ensure the combination is effective and well-tolerated.
5. Therapy and Lifestyle Modifications:
Therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can complement medication treatment for both ADHD and mental health concerns. Lifestyle adjustments, including exercise, proper nutrition, and stress management techniques, can also positively impact all three conditions.
Individuals with comorbid ADHD, anxiety, and depression require a personalized treatment approach. The “best” medication is the one that effectively addresses all three conditions while minimizing side effects and interactions. Open communication with a healthcare professional is crucial throughout the treatment journey to ensure that the chosen medications provide the desired benefits without causing any adverse effects.
World-class, Accredited, 5-Star Reviewed, Effective Mental Health Dual Diagnosis Programs. Complete Integrated Inpatient Rehab with Free Post Discharge Therapy Planning.
CALL (855) 940-6125End the Emotional Pain Rollercoaster. Gain Stability & Happiness Through Recovery Treatment. Start Mental Health Counseling Today. Get Free No-obligation Guidance by Behaviroal Health Specialists Who Understand Mental Health Recovery.
Signs ADHD Medication Dose Too High
Determining the correct dosage of ADHD medication is critical to effective treatment. An ADHD medication dose that is too high can lead to various unwanted effects and potentially worsen symptoms. Working closely with a healthcare professional to find the optimal dosage for an individual’s specific needs is essential. Here are some signs that the ADHD medication dose might be too high:
- Increased restlessness and agitation.
- Excessive nervousness.
- Insomnia or sleep disturbances.
- Rapid heartbeat.
- Heightened blood pressure.
- Intense mood swings.
- Heightened anxiety.
- Loss of appetite or weight loss.
- Physical discomfort (headaches, stomachaches).
- Reduced concentration.
- Overfocused or obsessive behavior.

If you notice any of these signs, consult your healthcare professional for guidance on adjusting your medication dose.
What Does ADHD Medication Do?
ADHD medication aims to alleviate the symptoms of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) by affecting neurotransmitter activity in the brain. The primary neurotransmitters targeted are dopamine and norepinephrine, which regulate attention, focus, impulse control, and motivation. The specific effects of ADHD medication can vary depending on the type of medication used, whether stimulant or non-stimulant. Here’s an overview of what ADHD medication does:
I apologize, but as a text-based AI, I can’t directly create tables in WordPress or any other platform. However, I can provide you with the information structured in a way that you can use to create a table manually in WordPress:
| Type of Medication | Primary Effects |
|---|---|
| Stimulant Medications | – Enhanced focus and attention – Reduced impulsivity – Decreased hyperactivity – Improved task management – Enhanced executive function |
| Non-Stimulant Medications | – Improved attention – Reduced impulsivity – Mood regulation – Enhanced task performance – Symptom management |
The effects of ADHD medication can vary from person to person. Finding the proper medication and dosage often requires careful monitoring and open communication with a healthcare professional. Additionally, while medication can be an essential tool, it is often most effective with behavioral therapies, lifestyle adjustments, and supportive strategies.
How Does Non-Stimulant ADHD Medication Work?
Non-stimulant ADHD medications work through different mechanisms than stimulant medications to alleviate the symptoms of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). These medications target neurotransmitter systems in the brain to improve attention, focus, impulse control, and other executive functions. Here’s how non-stimulant ADHD medication works:
- Atomoxetine (Strattera): Atomoxetine is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (NRI). It works by increasing the levels of norepinephrine, a neurotransmitter associated with attention and focus, in the brain. By blocking the reuptake of norepinephrine, atomoxetine enhances its availability in synapses, which can lead to improved attention, impulse control, and organization.
- Guanfacine (Intuniv) and Clonidine (Kapvay): Guanfacine and clonidine are alpha-2 adrenergic agonists. They work by stimulating specific receptors in the brain, leading to a decrease in norepinephrine release. This can be calming, reducing hyperactivity, impulsivity, and distractibility. Additionally, these medications can help regulate blood pressure and heart rate, contributing to a more focused and organized mindset.
Non-stimulant medications tend to have a more gradual onset of action than stimulants. They may take several weeks to reach their full therapeutic effect. While their mechanisms differ, their goal is to balance neurotransmitter activity in the brain, addressing the core symptoms of ADHD.
It’s essential to note that the effectiveness of non-stimulant medications varies from person to person. Finding the proper medication and dosage often involves a trial-and-error process under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Non-stimulant medications are generally considered when stimulant medications are not effective, are not tolerated due to side effects, or when there are concerns about their use due to medical history or potential interactions.
As with any medication, open communication with a healthcare provider is crucial to determine the most appropriate treatment approach based on an individual’s needs and circumstances.
Experience Transformative Recovery at the We Level Up Treatment Center.
See our authentic success stories. Get inspired. Get the help you deserve.



Start a New Life
Begin with a free call to a behavioral health treatment advisor. Learn more about our dual-diagnosis programs. The We Level Up treatment center network delivers recovery programs that vary by each treatment facility. Call to learn more.
- Personalized Care
- Caring Accountable Staff
- World-class Amenities
- Licensed & Accredited
- Renowned w/ 5-Star Reviews
We’ll Call You
Popular Non-Stimulant ADHD Medication FAQs
-
What are non-stimulant ADHD medications?
Non-stimulant ADHD medications are drugs used to treat Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) without relying on stimulant compounds. They work through different mechanisms to address inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity symptoms.
-
What are some common non-stimulant ADHD medications?
Common non-stimulant ADHD medications include Atomoxetine (Strattera), Guanfacine (Intuniv), and Clonidine (Kapvay). These medications target neurotransmitter systems to improve ADHD symptoms.
-
Who might consider non-stimulant ADHD medications?
Non-stimulant medications are often considered when stimulant medications are ineffective, not tolerated due to side effects, or when there are medical reasons to avoid stimulants.
-
How long does it take for non-stimulant medications to work?
Non-stimulant medications typically have a more gradual onset of action compared to stimulants. It might take several weeks to notice the full therapeutic effects.
Watch How to Improve Mental Health? 8 Steps & Tips for Maintaining Your Mental Wellbeing. Find Top Mental Health Tips & Anxiety Tips Advice from a Therapist.
Search Drug & Alcohol Rehab / Detox & Mental Health Non-Stimulant ADHD Medication. ADHD Medication for Adults. Topics & Resources
Sources
[1] What is ADHD? | CDC Examining ADD vs ADHD Learn More: ADHD Medication
[2] NIMH » Mental Illness (nih.gov) ADD vs ADHD Review Learn More: ADHD Medication
[3] NIMH » Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) (nih.gov) Learn More: ADHD Medication
[4] Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov) ADD vs ADHD Adults Review. Learn More: ADHD Medication
[5] ADHD: Reviewing the Causes and Evaluating Solutions – PMC (nih.gov) ADD vs ADHD in Adults Causes. Learn More: ADHD Medication
[6] What is mental health? Evidence towards a new definition from a mixed methods multidisciplinary, international survey – PMC (nih.gov) ADD vs ADHD Symptoms Learn More: ADHD Medication
[7] COMMON MENTAL HEALTH DISORDERS – Common Mental Health Disorders – NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov) ADD vs ADHD in Female Adults Learn More: ADHD Medication
[8] About Mental Health (cdc.gov)
[9] Information about Mental Illness and the Brain – NIH Curriculum Supplement Series – NCBI Bookshelf Learn More: ADHD Medication
[10] Effective Mood And Personality Disorder Treatment (welevelupnj.com)