By We Level Up FL Treatment Center | Editor Yamilla Francese | Clinically Reviewed By Lauren Barry, LMFT, MCAP, QS, Director of Quality Assurance | Editorial Policy | Research Policy | Last Updated: April 7, 2023
What is Schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is a serious mental condition that impacts a person’s thoughts, feelings, and actions. People with schizophrenia may seem like they have lost touch with reality, which causes significant distress for the individual, their family members, and friends. If left untreated, the symptoms of schizophrenia can be disabling and persistent. However, effective treatments are available. When provided in a timely, sustained, and coordinated manner, therapy and treatment can help affected individuals engage in work or school, achieve independence, and enjoy personal relationships [1].
A diagnosis of schizophrenia frequently follows the first episode of psychosis, when someone first displays symptoms of this mental illness. However, gradual mood, thinking, and social functioning changes often begin before the first episode of psychosis, usually starting in mid-adolescence. Schizophrenia can happen in younger children, but it is rare to emerge before late adolescence. Schizophrenia is treatable. Treatment with medicines and psychosocial support is effective.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO) [2], research has not identified one single factor that causes schizophrenia. It is thought that interaction between genes and various environmental factors may cause this mental disease. Psychosocial factors may also contribute to schizophrenia.
Schizophrenia causes affected individuals to view events in their life abnormally. Delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized thought are characteristic of this disease. Living with schizophrenia is challenging and demanding, as daily functioning can be severely affected. For several years, researchers have studied the schizophrenia causes, and the mental disease remains a mystery in many ways.
Research on Schizophrenia Causes
Comprehensive research has been conducted on schizophrenia causes to identify and improve treatment methods. For example, a study conducted by Harvard Medical School researchers in 2016 showed a genetic analysis of 65,000 people to determine what causes schizophrenia. It was discovered that the risk of such disease increases when distinct variants in a gene are passed down from one generation to another. In addition, the gene C4, which has a part connecting to the immune system, has been identified as playing a pivotal role in brain development abnormalities associated with schizophrenia.
A 2014 study led by researchers at the Stanley Center discovered that more than 100 regions in the brain could determine risk factors for schizophrenia. Several of those genes are connected to regulating dopamine, a neurotransmitter responsible for motivation, pleasure, and learning.
Integrated research efforts have led to significant breakthroughs in schizophrenic. It suggests that synaptic pruning during adolescence may be responsible for the onset of the mental disorder. Synaptic pruning is when the brain eliminates extra neurons and synaptic connections to improve neuronal transmission efficiency. This finding opens doors of hope that future treatments that slow down the synaptic pruning process may decrease the risk of developing schizophrenia. The research also helps to explain why people who have schizophrenia also have a thinner cerebral cortex.
Schizophrenia Causes
The exact schizophrenia causes are still unknown. Research suggests a combination of genetic, psychological, physical, and environmental factors can make an individual more likely to develop the condition. Some individuals may be predisposed to this disease, and an emotional or stressful life event might trigger a psychotic episode. However, it’s unknown why some individuals develop symptoms while others do not.
Increased Risk of Schizophrenia
Genetics
Schizophrenia seems to run in families, but no single gene is thought to be responsible. Different varieties of genes may make individuals more vulnerable to the condition. However, having these genes does not necessarily indicate you’ll develop schizophrenia.

Skip To:
Learn More:
- What Is a Co-occurring Dual Diagnosis Treatment Center? Why is dual diagnosis treatment vital for long-term Recovery?
- Drug Induced Schizophrenia, Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
- Is Schizophrenia Hereditary? Causes, Symptoms, Risk Factors & Therapies
- Schizophrenia and Heredity, Causes of Schizophrenia, Diagnosis & Best Treatment Options
- Schizophrenia Treatment, Signs, Symptoms & Causes
- Impulse Control Disorder: Definition, Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
- Relationship Depression, Symptoms, Causes and What To Do
- What Is Paranoia? Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
- Heart Palpitations Anxiety: Causes, Symptoms & Treatments
- Can Anxiety Cause Diarrhea? The Link, Causes & Treatments
Proof that the disorder is partly inherited comes from studies of twins. Identical twins share the same genes. In identical twins, if a twin develops schizophrenia, the other twin has a 1 in 2 chance of developing it. This is true even if they’re raised separately.
In non-identical twins with different genetic makeup, when one twin develops the disease, the other only has a 1 in 8 chance of developing the same condition.
While this is higher than in the general population, where the chance is about 1 in 100, it suggests genes are not the only factor influencing the development of schizophrenia.
Schizophrenia Fact Sheet
Schizophrenia Overview
A condition that impairs a person’s capacity for clear thought, feeling, and behavior.
Although the precise origin of schizophrenia is unknown, it is thought that a mix of genetics, environment and altered brain chemistry and structure may be at play.
Schizophrenia is characterized by disorganized speech or behavior, depressed participation in daily tasks, and ideas or experiences that appear disconnected from reality. Memory loss and attention problems could also be present.
Treatment is typically ongoing and frequently consists of a mix of prescription drugs, psychotherapy, and well-coordinated specialty care services.
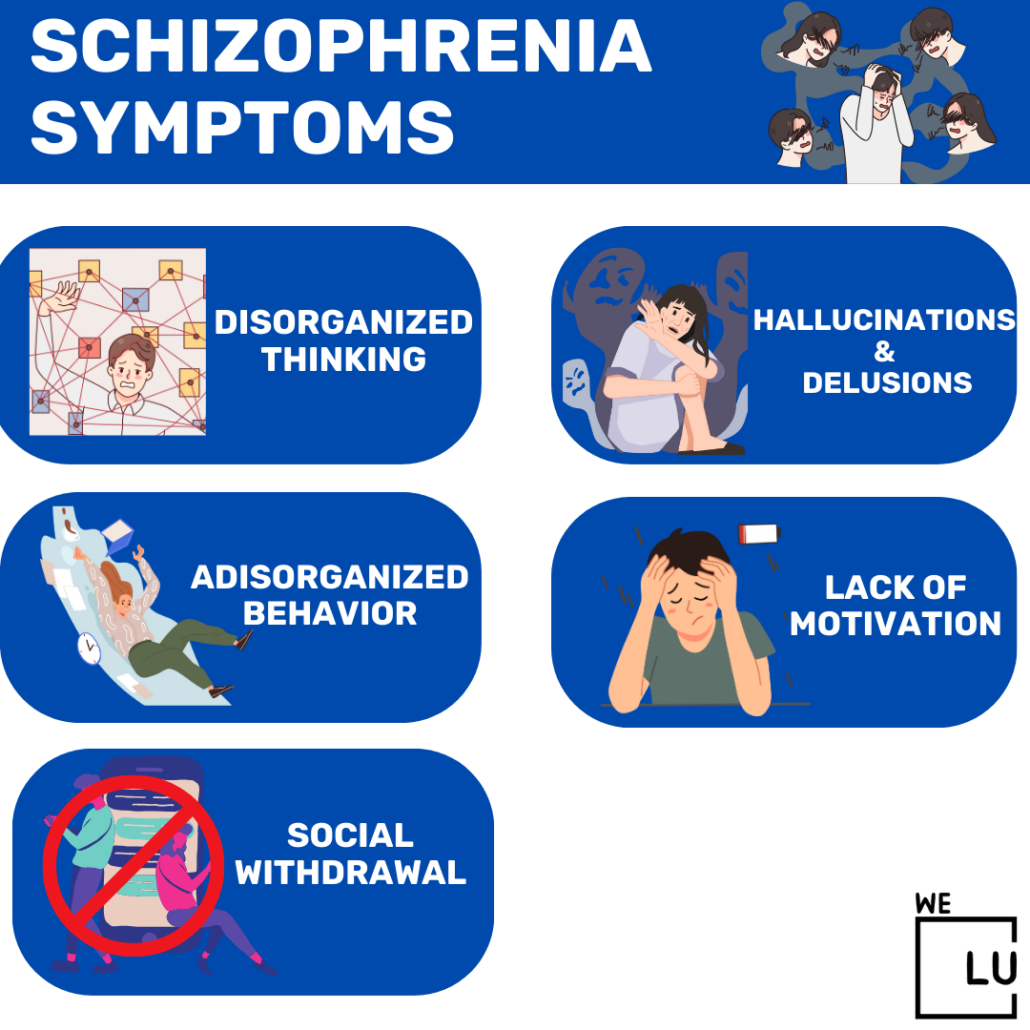
Schizophrenia Symptoms
Schizophrenia is characterized by disorganized speech or behavior, depressed participation in daily tasks, and ideas or experiences that appear disconnected from reality. Memory loss and attention problems could also be present.
Schizophrenia Treatments
Treatment is typically ongoing and frequently consists of a mix of prescription drugs, psychotherapy, and well-coordinated specialty care services.
Schizophrenia Statistics
A mental disorder called schizophrenia is characterized by disturbances in thought, perception, emotional responsiveness, and social interactions. Although each person’s experience with schizophrenia is unique, the condition is typically chronic and can be severe and incapacitating.
4.9%
With the risk being highest in the early stages of the illness, an estimated 4.9% of people with schizophrenia commit suicide, a rate significantly higher than that of the general population.
Source: National Insitute Of Mental Health
24 Million
Around 24 million globally, or 1 in 300 persons (0.32%), suffer from schizophrenia. Adults at this rate make up 1 in 222 individuals (0.45%). It does not occur as frequently as many other mental illnesses.
Source: World Health Organization
50%
Most people with schizophrenia do not currently have access to mental health services. An estimated 50% of patients in psychiatric hospitals have a diagnosis of schizophrenia.
Source: World Health Organization
Brain development
Studies of individuals with this mental illness have shown slight brain structure differences. These changes are not seen in everyone with schizophrenia and can happen in individuals who do not have a mental illness. But they suggest schizophrenia may partly be a disorder of the brain.
Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters are chemicals that carry messages between brain cells. There’s a connection between schizophrenia and neurotransmitters because medications that alter the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain are known to relieve some of the symptoms of schizophrenia.
Research suggests schizophrenia may be caused by a change in the level of 2 neurotransmitters: serotonin and dopamine. Some studies reveal an imbalance between the two may be the basis of the issue. Others have found a change in the body’s sensitivity to the neurotransmitters is part of the cause of schizophrenia.
Birth complications and Pregnancy
Research has shown individuals who develop schizophrenia are more likely to have undergone complications before and during their birth, such as:
- A low birth weight.
- Premature labor.
- A lack of oxygen (asphyxia) during birth.
It may be that these things have a subtle effect on brain development.
Viral Infections
Exposure to viruses is a contributing factor in the development of schizophrenia. There are a variety of traits of viruses that might make this possible. For example, viruses can:
- Attack certain brain regions and leave others intact.
- Alter specific processes within a brain cell without killing the cell.
- Infect someone and then lay dormant for many years before causing illness.
- Cause minor physical abnormalities, birth complications, and altered fingerprint patterns sometimes found in people with schizophrenia.
- Affect neurotransmitters.
It is also important to note that some antipsychotic agents are also antiviral agents, which can support the idea that viral infections can play a role in developing schizophrenic symptoms, particularly psychotic symptoms.
Schizophrenia Triggers
Because researchers don’t completely understand schizophrenia causes, there’s no sure way to prevent it. However, following your treatment plan can lessen the probability of relapse or aggravating symptoms if you’ve been diagnosed with this mental disorder.
Also, if you know that you’re at an increased risk for the mental disorder — such as by a genetic tie — you can avoid potential triggers or things that can cause symptoms. Triggers are things that can cause schizophrenia to develop in individuals who are at risk. These include:
Triggers are things that can cause schizophrenia to develop in individuals who are at risk. These include:
Stress
The main psychological triggers of schizophrenia are stressful life events, such as:
- Bereavement (death of a loved one).
- Losing your job or home.
- Divorce.
- The end of a relationship.
- Physical, sexual, or emotional abuse.
These types of experiences, although stressful, do not cause schizophrenia. However, they can trigger its development in someone already vulnerable to it.

These types of experiences, although stressful, do not cause schizophrenia. However, they can trigger its development in someone already vulnerable to it.
Drug abuse
Drugs do not directly cause schizophrenia, but studies have shown drug misuse increases the risk of developing the disease or a similar illness.
Certain drugs, particularly marijuana, cocaine, LSD, or amphetamines, may trigger symptoms of schizophrenia in people who are at risk.
Using illegal stimulants like cocaine and crystal meth can lead to psychosis and can cause a relapse in individuals recovering from an earlier episode.
Childhood trauma
Childhood trauma is also thought to be a contributing factor in developing schizophrenia. Some individuals with schizophrenia experience hallucinations related to abuse or neglect they experienced as children.
People are also more likely to develop schizophrenia if, as children, they experienced the death or permanent separation of one or both parents.
This kind of trauma is tied to various other adverse early experiences, so it’s still unclear if this trauma is a cause of schizophrenia or just associated with the condition.
Exposure to Toxins
Being exposed to harmful toxins is suggested to play a role in developing schizophrenia, even as early as during fetal development. Toxins that have been researched to show possible influence include alcohol and lead.
Exposure to lead during fetal development has been shown to greatly influence the likelihood of the development of schizophrenia and psychosis. Lead can be found in things such as:
- Gasoline.
- Paint.
- Tap water.
- Children’s toys.
Although measures have been taken in recent years to remove lead from the things we come in contact with every day, it is crucial to be aware that chemical lead can still be in our environment. For example, if a home was painted with lead paint before 1978, it can still release this toxin.
Treatment
Schizophrenia is a lifelong condition, but effective treatment can help a person manage the symptoms, prevent relapses, and avoid hospitalization.
Each person’s experience will differ, and a doctor will tailor the treatment to suit the individual.
Some potential treatment options include:
- Antipsychotic drugs. These can be for daily use or for less frequent use if the person opts for injectable medications, which can last up to 3 months between injections (depending on the medication) [3].
- Counseling. This can help a person develop coping skills and pursue their life goals.
- Coordinated special care. This integrates medication, family involvement, and education services holistically.
Some common medications for schizophrenia include:
- Risperidone (Risperdal).
- Olanzapine (Zyprexa).
- Quetiapine (Seroquel).
- Ziprasidone (Geodon).
- Clozapine (Clozaril).
- Haloperidol (Haldol).
Many drugs have adverse effects, including neurological symptoms and weight gain. Newer medications may have less severe side effects, however.
A person must continue their treatment plan, even if the symptoms improve. The symptoms may return if a person stops taking medication [4].
What is Schizophrenia? Video
We take a deep dive into the intricate world of Schizophrenia, shedding light on its multifaceted causes, risk factors, and potential triggers. Schizophrenia is a profound mental condition that affects countless individuals and their loved ones. Understanding the complexities of this disorder is essential for providing support and promoting effective treatments.
Most Popular Schizophrenia Causes FAQs
-
What is the cause for Schizophrenia?
If you are wondering, “what are the causes for schizophrenia?”, “what cause schizophrenia?”, “what are causes of schizophrenia?”, “what are the social causes of schizophrenia?”, “what are the environmental causes of schizophrenia?”, “what are the biological causes of schizophrenia?”, “what is schizophrenia caused by?”, “what causes paranoid schizophrenia?”, “what are the causes of paranoid schizophrenia?”, “what is the cause of schizophrenia?”, “how is schizophrenia caused?”, “what can cause schizophrenia?”, “what are paranoid schizophrenia causes?”, or “what are the causes of schizophrenia?”, the answer is there is no known precise cause of schizophrenia. According to research, a person may be more susceptible to acquiring the illness if a combination of physical, genetic, psychological, and environmental factors are present.
-
Can drugs cause Schizophrenia?
If you are wondering, “can drug use cause schizophrenia?”, “is schizophrenia caused by drugs?”, or “do drugs cause schizophrenia?”, the answer is although studies have indicated that drug abuse raises the likelihood of getting schizophrenia or a comparable disorder, drugs do not directly cause schizophrenia. Among those who are vulnerable, some drugs, particularly cannabis, cocaine, LSD, or amphetamines, may cause symptoms of schizophrenia.
-
Can trauma cause Schizophrenia?
Suppose you wonder, “can schizophrenia be caused by trauma?”. In that case, the answer is trauma may alter the body and impact neurotransmitters in the brain, raising the possibility of schizophrenia or psychotic symptoms. Schizophrenia can be brought on by childhood trauma in those predisposed to it, and symptoms might appear between late adolescence and the early thirties.
-
What causes Schizophrenia in the brain?
According to research, a change in the neurotransmitters serotonin and dopamine levels may be the root of schizophrenia. Several studies say an imbalance between the two may be the issue’s root. Others have discovered that schizophrenia is partially caused by a shift in the body’s sensitivity to neurotransmitters.
-
Can weed cause Schizophrenia?
If you are wondering, “does weed cause schizophrenia?”, the answer is individuals who use marijuana are more prone to experience short-term psychosis (a false perception of reality, hallucinations, and paranoia) and chronic mental illnesses like schizophrenia (a mental illness where people might see or hear things that are not there).
-
Can alcohol cause Schizophrenia?
Medical research has conclusively linked alcohol usage and schizophrenia. Alcohol can exacerbate schizophrenia symptoms as well as produce symptoms that resemble the disease. Although there may be a connection between alcohol and schizophrenia, it is not believed that drinking causes schizophrenia.
-
Can PTSD cause Schizophrenia?
A number of genes have been linked to PTSD by a significant genome-wide association study (GWAS), and these genes also increase the likelihood of developing schizophrenia.
-
Can psychedelics cause Schizophrenia?
Studies have also revealed a genetic susceptibility to schizophrenia in those who develop schizophrenia after undergoing substance-induced psychosis.
-
Can smoking cause Schizophrenia?
Although most smokers do not get schizophrenia, smoking may still increase the risk. One Israeli study found that compared to nonsmokers, people who smoked more than 10 cigarettes daily had a more than doubled risk of getting schizophrenia.
-
Can stress cause Schizophrenia?
Events that are extremely stressful or life-altering might occasionally cause schizophrenia. This could involve harassment or being abused. losing a close friend or relative.
How We Can Help
Whether this is your first and last treatment program, or even if you invested years of your time in and out of other therapy programs, we can make you feel at peace again. The We Level Up FL Behavriaol Center is unique in offering unparalleled evidence-based programs. Along with ultra modern therapeutic modalities to advance mental health treatment outcomes. Moreover, the We Level Up FL Mental Health Center also offers:
— Quick intake appointments. And in some cases, where warranted, same-day admissions.
— Comfortable & safe settings with attentive staff in modern facilities with amenities to promote recovery.
— In-house Teams of specialists trained to deal with complex multi-diagnosis mental illness and its corresponding underlying triggers.
— Complimentary critical family and alumni programs so you’ll have support while in treatment and beyond. Even after you leave.
— We accept most insurance and offer free benefits verification without any obligation.
— Secondary co-occurring dual diagnosis treatment programs.
— Intensive residential inpatient treatment.

Visit the We Level Up FL behavioral recovery center & talk with faculty members. Tour the facility and see why we’re an established complex diagnosis treatment center. Visit patient community areas and lounges. There you can find outdoor areas for patients to recuperate and rebound. Witness how you can feel at home at We Level Up FL’s behavioral center. The answers to your recovery should include locating a reputed and well-qualified therapy program for your treatment.
If you have questions regarding your diagnosis or want licensed guidance or therapy for the schizophrenia causes, please get in touch with us.
How to Improve Mental Health Including Schizoprehnia? 8 Steps & Tips for Maintaining Your Mental Wellbeing Video
8 Steps for Mental Wellbeing & How To Improve Mental Health In The Workplace
1. Staying Positive
2. Practicing Gratitude
3. Taking Care of Your Physical Health
4. Connecting With Others
5. Developing a Sense of Meaning and Purpose in Life
6. Developing Coping Skills
7. Meditation
8. Relaxation Techniques